How to Create a Custom Work Item Handler in jBPM
Custom Work Item Handlers help us connect to external systems and execute business logic.

You work for a demanding, yet friendly credit card company.
And you’ve almost finished building their business process in jBPM.
Your promotion is so close you can taste it..
But when you scroll through the list of service tasks, you can't find one to save the process information to your database.
Are you doomed? No. You can create a work item handler to..
Connect with External Services
If you want your process to connect to external systems (databases, web services) or execute special business logic, then you can..
Create a Custom Work Item Handler
We’ll create a custom work item handler in JBoss Dev Studio. But you can also do this in Business Central.
What You’ll Need
1: JBoss Developer Studio w/ JBoss EAP 6.4
- EAP: Download here
- JBoss Maven Repositories (Section 1: Steps 4-7)
2: Basic Maven & BPM knowledge
3: JBPM Eclipse modeler. Download here
Create a Custom Service Task
Step 1: Download the simple-process-workitemhandler project
- This project contains a bpm process that prints “Hello World”
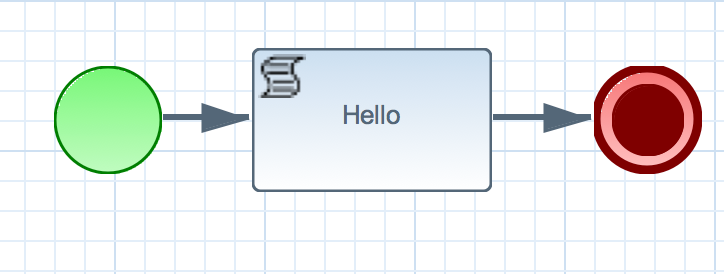
- We’ll change this script task to a custom task that executes our logic
- Import this project in JBoss Developer Studio
Step 2: Define a Work Item
- Create a file src/main/resources/META-INF/MyWorkDefinitions.wid
import org.drools.core.process.core.datatype.impl.type.StringDataType;
[
[
"name" : "Random Number",
"parameters" : [
"Message" : new StringDataType(),
],
"displayName" : "Random Number",
"icon" : "icon-info.gif"
]
]- Here we define the name of our task, a parameter and an icon
Step 3: Cleanup our process
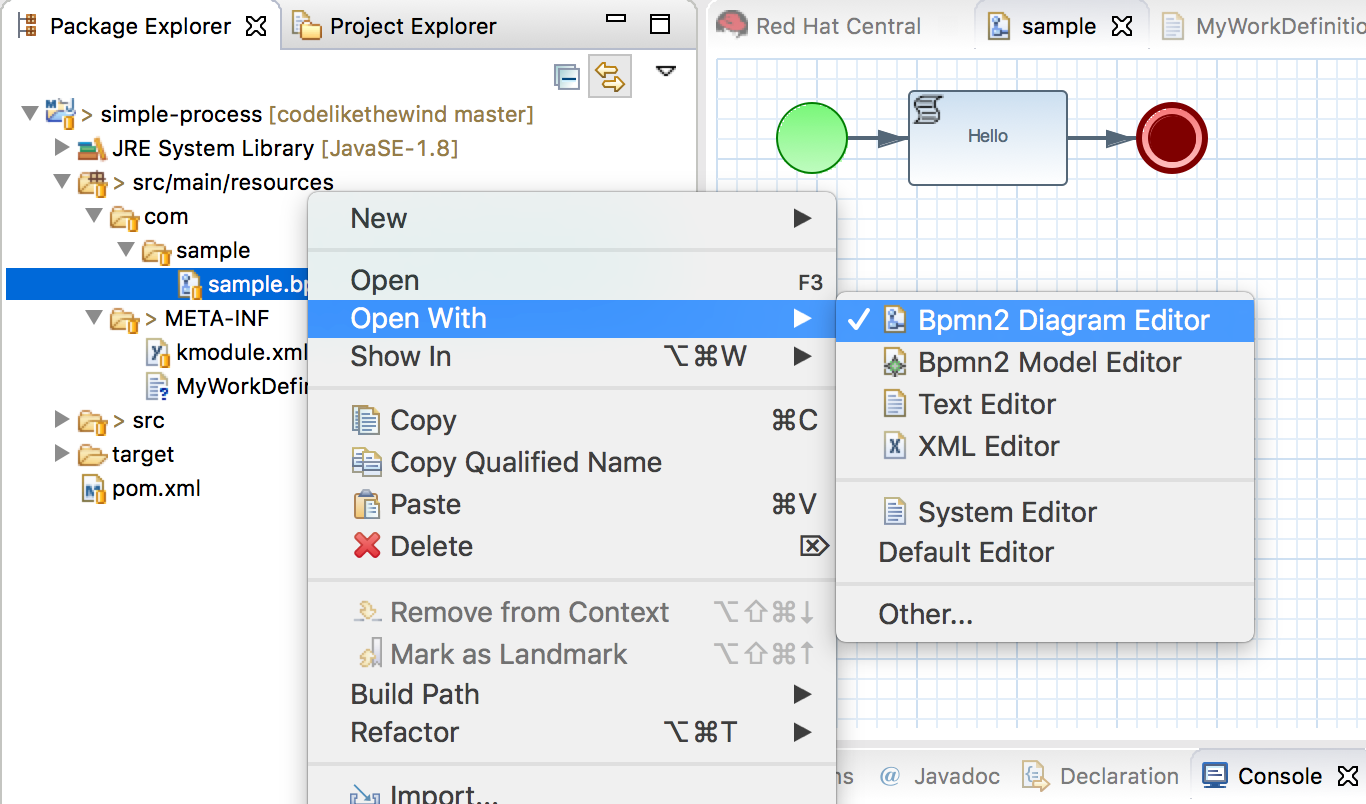
- Right click com/sample/sample.bpm → Open with → BPMN Diagram Editor
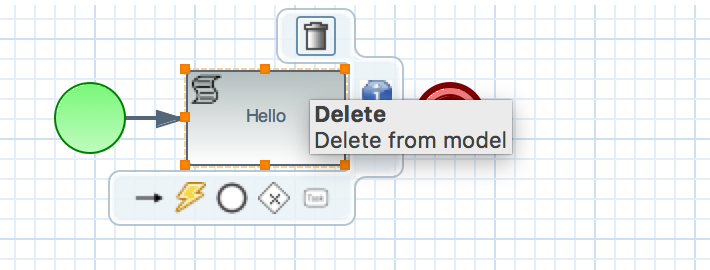
- Delete the script task and end node.
Step 4: Create a Custom Service Task
- Create a Random Number Task
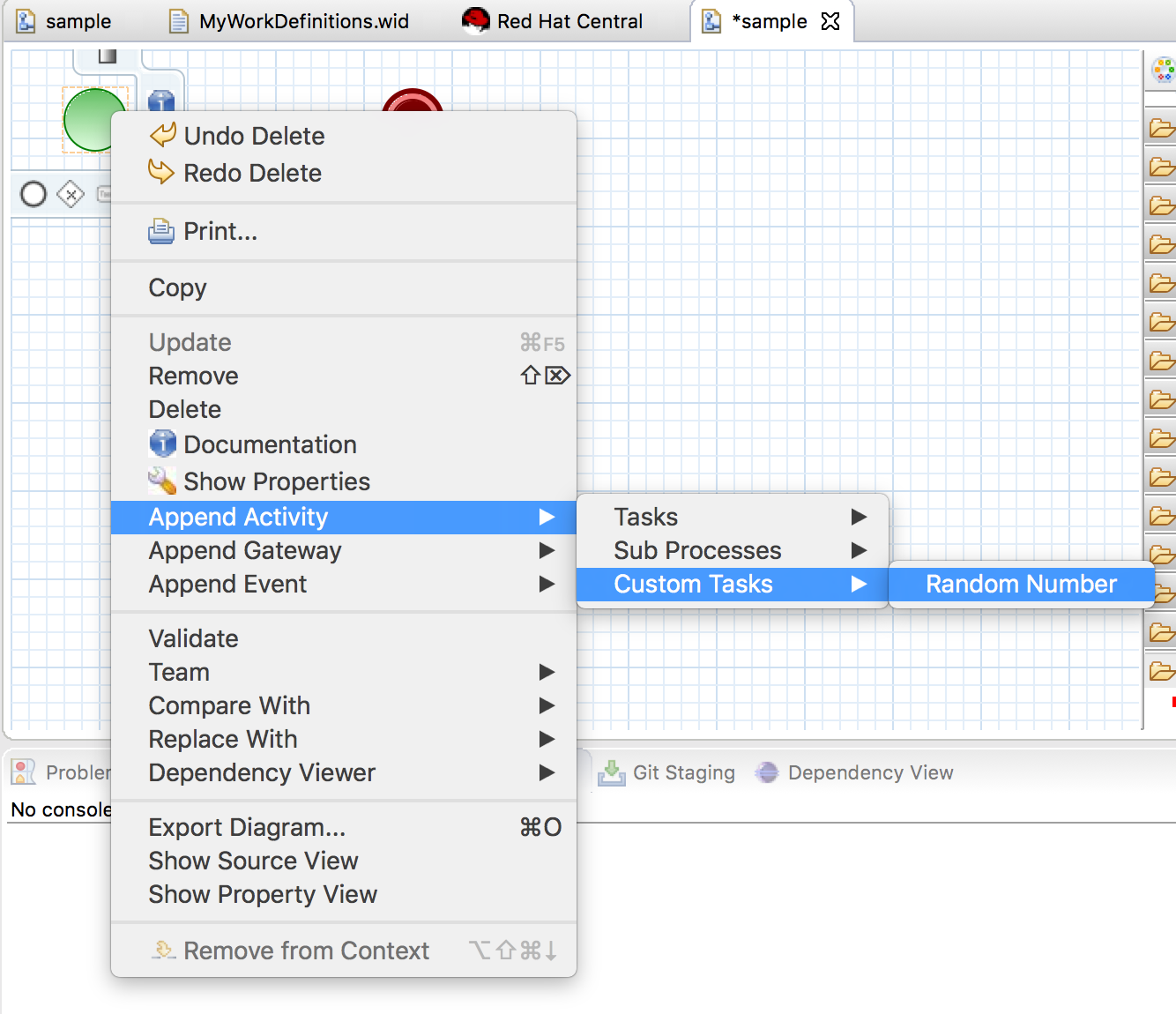
- To add a parameter, double click the Random Number task
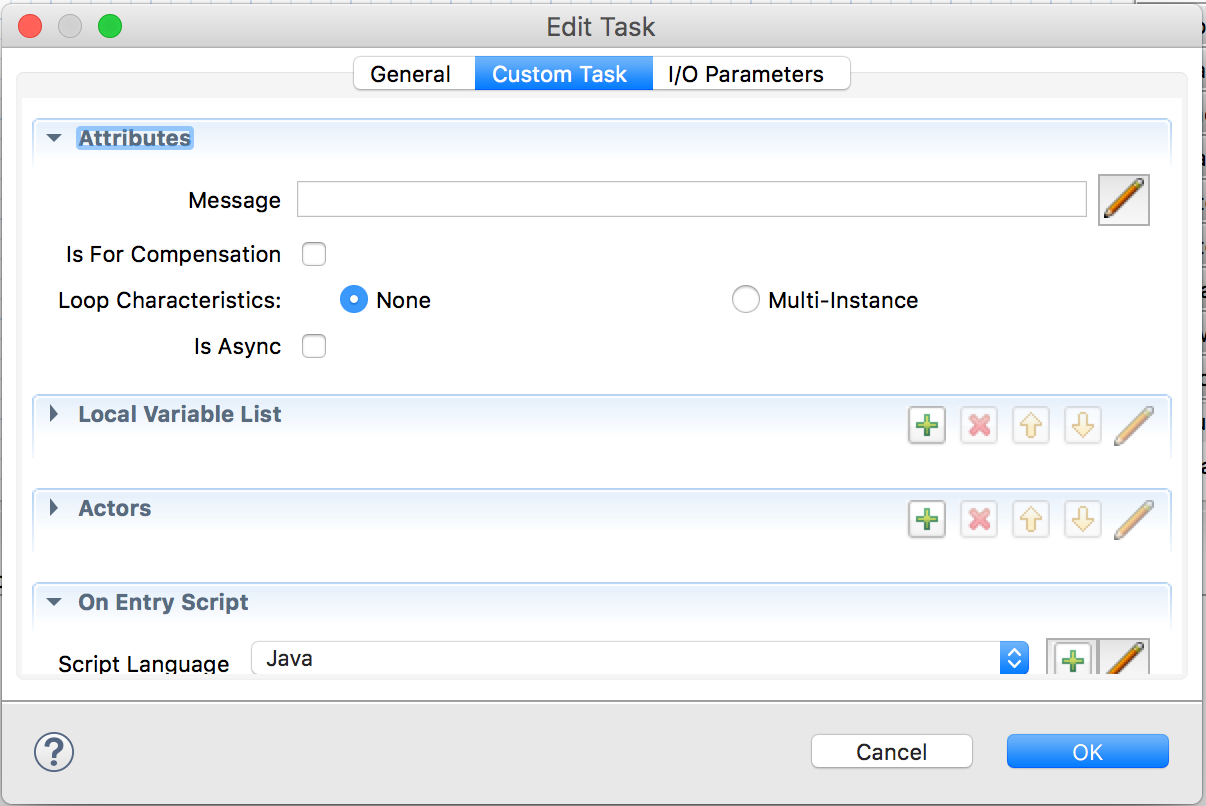
- Click the pencil next to Message
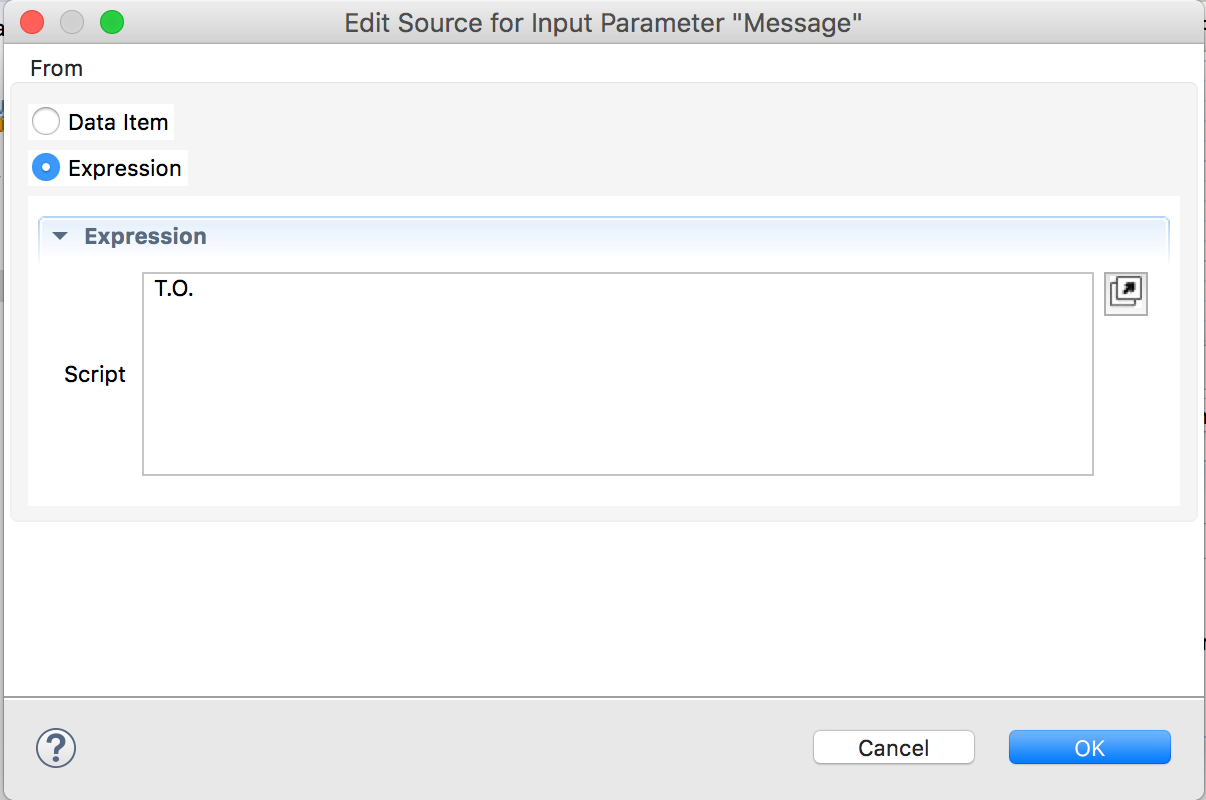
- Select ‘Expression’ and type your name. Click Ok
- Save the process
Step 5: Add a Terminate Node
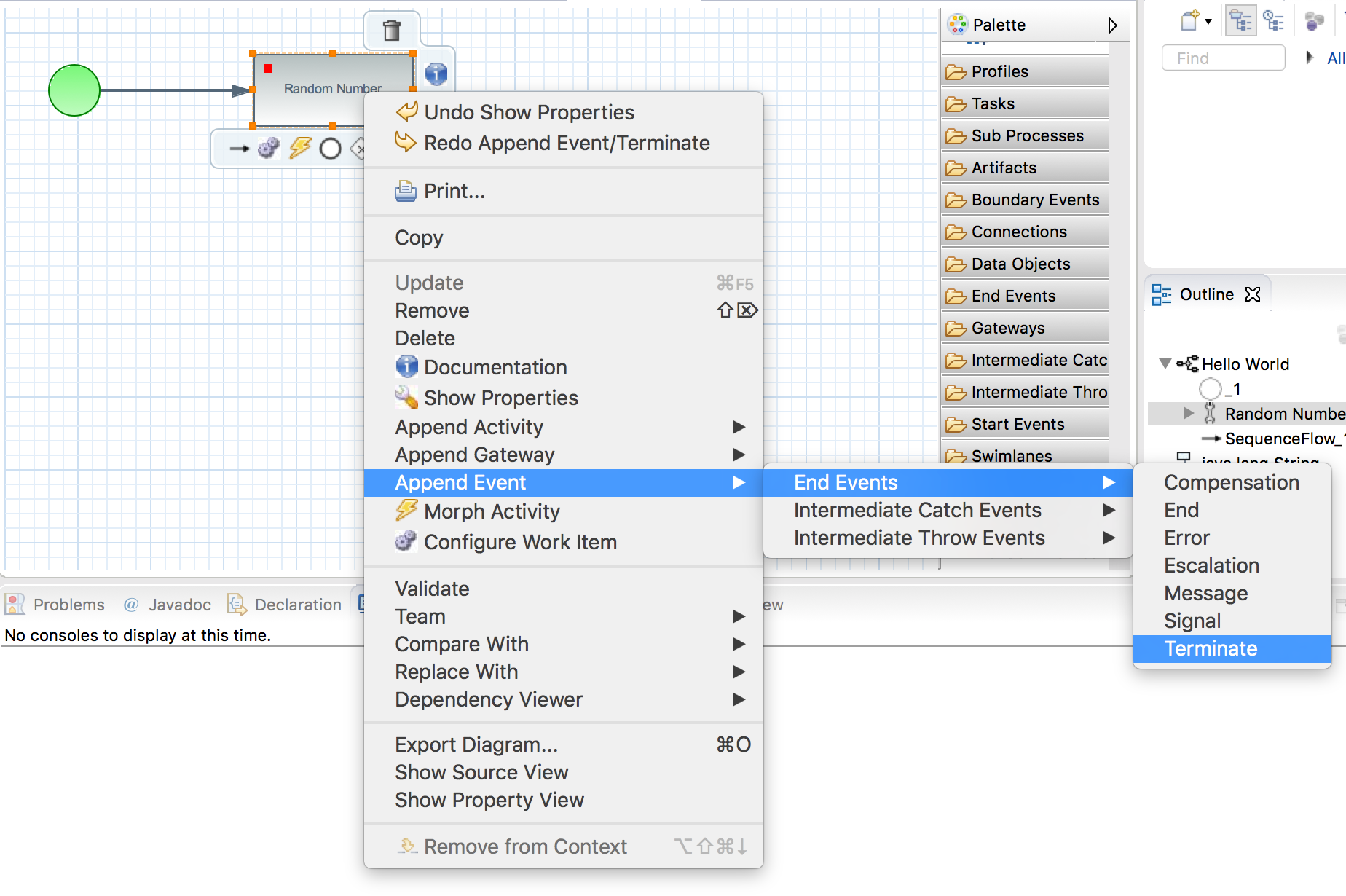
Step 6: Connect the Service Task and Work Item Handler
- Create a file /src/main/resources/META-INF/kie-deployment-descriptor.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<deployment-descriptor xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.jboss.org/jbpm deployment-descriptor.xsd" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<work-item-handlers>
<work-item-handler>
<resolver>mvel</resolver>
<identifier>new org.codelikethewind.workitemhandler.RandomWorkItemHandler()</identifier>
<parameters/>
<name>Random Number</name>
</work-item-handler>
</work-item-handlers>
</deployment-descriptor>- This registers our service task to the work item handler that we’ll create next.
Step 7: Build the project
- Right click your project (simple-process) -> Run as -> Maven Build.
Goals: clean installCreate a WorkItemHandler
Step 1: Download the embedded-process-workitemhandler project
- This web app runs the bpm process we just worked on. When we’re done, that process will execute a custom work item handler
Step 2: Create a Custom Work Item Handler
- In package org.codelikethewind.workitemhandler, create a class called RandomWorkItemHandler
public class RandomWorkItemHandler implements WorkItemHandler {
}- Implement the execute and abort methods
@Override
public void abortWorkItem(WorkItem workItem, WorkItemManager manager) {
manager.abortWorkItem(workItem.getId());
}
@Override
public void executeWorkItem(WorkItem workItem, WorkItemManager manager {
Random rand = new Random();
int n = rand.nextInt(50) + 1;
Object name = workItem.getParameter("Message");
System.out.println("Hi " + name + ", your random number is: " + n);
manager.completeWorkItem(workItem.getId(), null);
}Step 3: Build the project
- Right click your project (embedded-process-workitemhandler) -> Run as -> Maven Build.
Goals: clean installRun the Process
Step 1: Deploy the simple-embedded-process
- Steps 1 & 2 of Method 1 here
Step 2: Start the process
Step 3: Check your server logs
- If your process prints out a random number, you’ve successfully built a custom work item handler!
Recap
Create a Custom Service Task
- We defined the structure of our work item -- a custom task in your process. It has a name, one parameter, and an icon.
- We added the custom task to our process and filled in a parameter
- We created a deployment descriptor to connect this service task to the work item handler.
Create a WorkItemHandler
- We created a custom work item handler to print a random number
- Our Work Item Handler is simple, but you can implement any complex logic.
Run the Process
- Once the process hits our service task, the execute() method in RandomWorkItemHandler will run
For Business Logic, Not Data
Use work item handlers (the java class) to run business logic, not create data. Your data should be passed in as a parameter to your custom work item (the service task).
This makes your process easy to update, test, and maintain.
So..
- Custom Work Item Handlers help us connect to external services or execute business logic
- We define a work item (service task), a work item handler (the implementation), and run it in our process
- Use work item handlers for logic, not data!
Source Code & Useful Links
- Finished projects: simple-process-workitemhandler & embedded-process-workitemhandler
- Official jBPM Documentation of Custom Service Tasks
- Creating Work Item Handlers in Business Central
Happy Coding!
-T.O.